The definition of a Hot Summer
A hot summer refers to a season characterized by above-average temperatures and prolonged periods of heat. It typically occurs in regions where the climate experiences significant temperature variations throughout the year, with summer being the warmest season. A hot summer is marked by high temperatures, often accompanied by intense sunlight and minimal rainfall.
During a hot summer, temperatures can reach or exceed the average seasonal highs, creating hot and sometimes sweltering conditions. This can have various impacts on the environment, ecosystems, and human activities. It can affect agriculture, water resources, energy demand, and outdoor recreational activities. Heatwaves, which are extended periods of excessively hot weather, are also common during a hot summer.
Hot summers can vary in intensity and duration depending on geographical location, climate patterns, and other factors. They may be influenced by climate change, which can contribute to more frequent and severe heat events. It is important to take necessary precautions during hot summers to protect oneself from heat-related illnesses and to ensure the well-being of people, animals, and plants affected by extreme temperatures.
Global Warming Effects
Over the past 20 years, the average global temperature has risen significantly due to human activities and the accumulation of greenhouse gases. Scientific studies and data confirm a temperature increase of approximately 1.1 degrees Celsius since the late 19th century. This rise in temperature has resulted in alarming consequences, including melting ice caps, sea-level rise, more frequent and intense heat waves, altered precipitation patterns, and increased risks of extreme weather events. These changes impact various sectors such as agriculture, water resources, energy production, and public health. To mitigate further temperature rise, international efforts like the Paris Agreement focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to sustainable practices. Monitoring and understanding these temperature trends highlight the urgent need for collective action to address climate change and protect our planet’s future.

Can we stand the heat?
Long hot summers can have various effects on individuals, both physically and psychologically. While it’s not accurate to say that they directly drive a person crazy, extreme heat and prolonged exposure to hot weather can impact mental well-being and contribute to certain challenges. Here are some factors to consider:
- Heat-related illnesses: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to heat exhaustion or heatstroke, which can cause confusion, disorientation, and in severe cases, delirium. These physical effects can indirectly affect mental well-being.
- Sleep disturbances: Hot weather can make it difficult to sleep comfortably, leading to sleep deprivation. Lack of quality sleep can contribute to irritability, mood swings, and cognitive difficulties.
- Agitation and irritability: High temperatures can make people feel uncomfortable, sweaty, and fatigued, which may contribute to irritability and shorter tempers.
- Reduced motivation and productivity: Extreme heat can drain energy levels and reduce motivation, making it harder to focus, work, or engage in activities. This can lead to frustration and a sense of decreased productivity.
- Impact on mental health conditions: For individuals already dealing with mental health conditions such as anxiety or depression, hot weather can exacerbate symptoms and make it more challenging to manage their well-being.
It’s important to note that the effects of heat on mental well-being can vary from person to person, and not everyone will experience significant negative impacts. Additionally, there are strategies to mitigate the potential challenges, such as staying hydrated, seeking shade, using cooling methods, and practicing self-care. If someone is experiencing significant distress or mental health concerns due to heat or other factors, it is advisable to seek support from healthcare professionals or mental health providers who can offer appropriate guidance and assistance.
How much can the body have
The human body has a remarkable ability to regulate and withstand heat to a certain extent. The specific heat tolerance varies among individuals and can be influenced by factors such as age, overall health, fitness level, acclimatization, and hydration status. Here are some general guidelines:
- Core Body Temperature: The normal core body temperature for humans is around 98.6°F (37°C). The body has mechanisms to regulate and maintain this temperature within a narrow range, even when exposed to varying external temperatures.
- Heat Tolerance: The body can tolerate a wide range of temperatures, but excessive heat can strain its thermoregulatory systems. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures, especially when combined with high humidity, can lead to heat-related illnesses such as heat exhaustion and heatstroke.
- Heat Index: The heat index takes into account both temperature and humidity to assess how the body perceives the combined effect. It provides an indication of how hot it feels to the human body and can help assess the risk of heat-related illnesses.
- Individual Variations: Heat tolerance varies among individuals. Factors such as age, fitness level, and pre-existing health conditions can affect how well someone can withstand heat. Elderly individuals, children, and those with certain medical conditions may be more susceptible to heat-related illnesses.
- Acclimatization: The body can gradually adapt to higher temperatures through acclimatization. Regular exposure to heat allows the body to make physiological adjustments to improve heat tolerance and reduce the risk of heat-related illnesses.
- Hydration: Adequate hydration is crucial for heat tolerance. Staying hydrated helps regulate body temperature and supports the body’s cooling mechanisms through sweating.
- Heat Perception: Perception of heat can vary among individuals. Factors such as clothing, activity level, and personal comfort preferences influence how individuals perceive and respond to heat.
It’s important to note that extreme heat conditions can be dangerous and potentially life-threatening. It is recommended to follow guidelines for heat safety, such as staying hydrated, seeking shade, wearing appropriate clothing, and avoiding strenuous activities during peak heat hours.
What if a human is overheated?

When treating overheated individuals, prompt action is vital to manage heat-related illnesses. Here are steps to help treat someone who is overheated: Move to a cool area and remove excess clothing. Hydrate the person with cool water or electrolyte-containing drinks. Use cooling measures such as wetting the skin, applying cold packs, and using fans to promote airflow. Monitor vital signs and seek medical assistance if symptoms worsen or indicate severe heatstroke. Encourage rest and avoid strenuous activities. Prevention is essential, so stay hydrated, avoid prolonged exposure to extreme heat, wear appropriate clothing, and take breaks in cool or shaded areas. Promptly addressing overheating can help prevent complications and ensure the individual’s well-being. If symptoms persist or worsen, seek professional medical help immediately.
Where are the extremes now?
Climate change affects different regions in various ways, and its impact on heat levels can vary. While it’s challenging to pinpoint specific countries as the “most” affected, several regions are experiencing significant heat-related challenges due to climate change. Here are some areas that have been notably impacted:
- Middle East and North Africa: Countries in this region, including Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and UAE, face extreme heat waves with temperatures often exceeding 50°C (122°F). These high temperatures pose risks to human health, agriculture, and ecosystems.
- South Asia: Countries like India and Pakistan regularly experience scorching temperatures, particularly during heat waves. Heat-related deaths and heat stress on vulnerable populations, along with impacts on agriculture and water resources, are major concerns in this region.
- Sub-Saharan Africa: Many countries in Sub-Saharan Africa, such as Niger, Chad, and Sudan, are highly susceptible to heat waves and rising temperatures. These conditions can exacerbate existing challenges related to water scarcity, food security, and public health.
- Australia: Australia has faced numerous extreme heat events and prolonged heatwaves, leading to devastating bushfires, heat-related illnesses, and impacts on ecosystems. Cities like Sydney and Melbourne have experienced record-breaking temperatures.
- Southern Europe: Countries in Southern Europe, including Spain, Italy, and Greece, have witnessed rising temperatures, heat waves, and drought conditions. These factors can have adverse effects on agriculture, water availability, and tourism.
It’s important to note that climate change impacts are multifaceted and not limited to heat alone. Rising temperatures can interact with other factors such as sea-level rise, extreme weather events, and changing precipitation patterns, further exacerbating the overall challenges faced by different regions.
Addressing climate change requires global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote sustainable practices, and adapt to the changing climate. International collaborations and policies aimed at mitigating and adapting to climate change are crucial in minimizing its impacts on vulnerable regions.
Can we blame the sun?
While the sun does have an impact on Earth’s temperature, it is not the main driver behind the recent global temperature rise. Human activities, particularly the emission of greenhouse gases from burning fossil fuels, are the primary cause of current global warming. Although variations in solar activity can influence regional and short-term climate patterns, extensive scientific research and data analysis consistently show that human-induced greenhouse gas emissions have a far greater impact on the observed global temperature increase over the past century. Climate models and historical data support this conclusion. It’s important to recognize that while the sun’s influence on temperature is present, the sustained and significant global temperature rise is predominantly driven by human activities. Addressing and reducing greenhouse gas emissions remains crucial in mitigating the effects of climate change.
The sun is good for sales online, right?
Heat can indeed have an impact on online spending behavior, although the relationship between the two is complex and influenced by various factors. Here are a few key considerations to consider:
- Seasonal trends: Hot weather often coincides with certain seasons, such as summer in many regions. Seasonal changes can affect consumer behavior, including online spending patterns. During warmer months, people may be more inclined to purchase items related to outdoor activities, travel, summer fashion, and home cooling products.
- Comfort and convenience: High temperatures may discourage people from engaging in physical shopping at brick-and-mortar stores, leading them to turn to online shopping as a more comfortable and convenient alternative. The ease of browsing and purchasing from the comfort of your home can be particularly appealing during hot weather.
- Indoor activities: Extreme heat can limit outdoor activities, leading individuals to spend more time indoors. This increased indoor time can lead to more online browsing and shopping as a form of entertainment and leisure.
- Seasonal promotions and sales: Retailers often offer special promotions, discounts, and summer sales to attract customers during the hotter months. These marketing strategies can influence online spending behavior by creating a sense of urgency and enticing consumers to make purchases.
- Regional variations: The impact of heat on online spending may vary across regions due to climate variations, cultural differences, and individual preferences. Regions with particularly hot climates may experience more pronounced effects on online spending habits.
It’s important to note that while there may be correlations between heat and online spending behavior, other factors such as personal finances, consumer preferences, marketing strategies, and global events also significantly influence online spending patterns. Therefore, it’s necessary to consider a holistic view of these factors to gain a comprehensive understanding of consumer behavior in the online marketplace.
10 Must-Know Facts about the Sun!
- The sun is a star located at the center of our solar system. It is a nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, primarily composed of hydrogen and helium.
- It is about 4.6 billion years old and is roughly halfway through its estimated 10-billion-year lifespan.
- The sun is incredibly massive, accounting for more than 99.8% of the total mass of the solar system.
- It generates energy through nuclear fusion, where hydrogen atoms combine to form helium, releasing a tremendous amount of heat and light in the process.
- The sun’s surface temperature is about 5,500 degrees Celsius (9,932 degrees Fahrenheit). However, its core temperature reaches an astonishing 15 million degrees Celsius (27 million degrees Fahrenheit).
- Solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs) are powerful eruptions of energy and particles from the sun’s surface. They can cause geomagnetic storms and impact satellite communications and electrical systems on Earth.
- The sun’s magnetic activity follows an 11-year cycle, known as the solar cycle. This cycle is characterized by variations in sunspots, solar flares, and solar radiation levels.
- Sunspots are dark, cooler areas on the sun’s surface caused by intense magnetic activity. They often occur in pairs or groups and can be many times larger than Earth.
- Sunlight takes approximately 8 minutes and 20 seconds to reach Earth, traveling at a speed of about 299,792 kilometers (186,282 miles) per second.
- The sun’s energy is essential for life on Earth. It provides heat and light for photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy, enabling the growth of plants and the production of oxygen.
Where not to go in summer

It’s important to note that visiting these hot locations during summer can be hazardous due to the extreme temperatures. Adequate research, preparation, and precautions, such as carrying sufficient water, appropriate clothing, and consulting local authorities or guides, are essential for ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience.
- The Danakil Depression, Ethiopia: Known as one of the hottest places on Earth, this remote region experiences scorching temperatures year-round. With its lava lakes, colorful hot springs, and unique geology, it offers an otherworldly experience but is challenging to access due to its remote location and harsh desert conditions.
- Death Valley, United States: Located in California, Death Valley holds the record for the highest temperature ever recorded on Earth. It features vast salt flats, rugged mountains, and unique desert landscapes. Despite being a popular tourist destination, the extreme heat during summer makes it a challenging place to visit without proper preparation and precautions.
- Rub’ al Khali (Empty Quarter), Saudi Arabia: The largest continuous sand desert in the world, Rub’ al Khali is known for its expansive dunes and extreme temperatures. With limited infrastructure and services, accessing this inhospitable desert during the summer can be difficult and dangerous due to the blistering heat and harsh environment.
- Kebili, Tunisia: Situated in the Sahara Desert, Kebili experiences extremely high temperatures during summer. It offers a glimpse into traditional desert life with its oasis, ancient ksour (fortified villages), and sand dunes. However, the challenging desert terrain and limited transportation options make it less accessible for casual visitors during the hottest months.
- Sonoran Desert, Mexico, and United States: Stretching across southwestern North America, the Sonoran Desert is known for its diverse ecosystems and extreme summer temperatures. It is home to iconic species like the saguaro cactus and offers opportunities for outdoor activities. However, the searing heat and remote locations within the desert can present challenges for visitors, requiring careful planning and preparation.
Protect yourself against the heat

Protecting yourself from heat is essential to prevent heat-related illnesses such as heatstroke or dehydration. Here are some tips to help you stay safe in hot weather:
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day, even if you don’t feel thirsty. Avoid or limit drinks that can dehydrate you, such as caffeinated or alcoholic beverages.
- Dress appropriately: Wear lightweight, loose-fitting, and light-colored clothing made of breathable fabrics like cotton or linen. This helps your body stay cool by allowing sweat to evaporate.
- Seek shade: Stay in shaded areas as much as possible, especially during the hottest hours of the day, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. If shade is limited, use an umbrella or wear a wide-brimmed hat to protect yourself from direct sunlight.
- Use sunscreen: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF (at least 30) on all exposed skin, including your face, arms, and legs. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if you’re swimming or sweating.
- Stay indoors during peak heat: If possible, limit outdoor activities during extreme heat conditions. Use air conditioning or fans to keep your living space cool. If you don’t have access to air conditioning, consider visiting public places with air conditioning, such as shopping malls or libraries.
- Cool down: Take cool showers or baths, use wet towels on your neck or forehead, or use a handheld fan or misting spray to help lower your body temperature.
- Avoid strenuous activities: Minimize physical exertion during hot weather, especially during the peak heat hours. If you must engage in physical activities, do them during the cooler parts of the day and take frequent breaks in shaded areas.
- Check on others: Keep an eye on family members, friends, and neighbors, especially those who are more vulnerable to heat, such as young children, older adults, and individuals with chronic illnesses. Offer assistance if needed.
- Be mindful of your pets: Ensure your pets have access to shade and plenty of fresh water. Never leave them in a parked car, as temperatures can rise rapidly, leading to heatstroke.
- Listen to your body: Pay attention to any signs of heat-related illness, such as dizziness, nausea, rapid heartbeat, or confusion. If you experience severe symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
By following these guidelines, you can help protect yourself from the dangers of excessive heat and enjoy a safer and more comfortable experience in hot weather.
Why Wear Sunscreen?
Sunscreen is a vital product that helps safeguard the skin against the damaging effects of the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation. It accomplishes this by absorbing, reflecting, or scattering the UV rays, preventing them from penetrating the skin and causing harm. The primary benefits of sunscreen include:
- UV Protection: Sunscreen acts as a protective barrier between the skin and the sun’s harmful UV radiation, preventing sunburn, premature aging, and skin damage.
- Sunburn Prevention: Sunburn occurs when the skin is exposed to excessive UVB rays. Applying sunscreen with a high sun protection factor (SPF) significantly reduces the risk of sunburn by blocking or reducing the intensity of UVB radiation.
- Skin Cancer Prevention: Prolonged exposure to UV radiation increases the risk of skin cancer. Regular use of sunscreen helps lower this risk by providing a shield against both UVB and UVA rays, which are associated with skin cancer development.
- Anti-Aging Effects: UV radiation accelerates skin aging by breaking down collagen and elastin fibers, resulting in wrinkles and sagging. Sunscreen helps slow down this process by protecting the skin from UV-induced damage and preserving its youthful appearance.
- Hyperpigmentation Prevention: UV radiation can trigger excess melanin production, leading to hyperpigmentation such as dark spots and uneven skin tone. Sunscreen helps prevent and reduce the appearance of these pigmentation irregularities by blocking the UV rays responsible for their formation.
To ensure effective protection, choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen that guards against UVA and UVB rays. Apply sunscreen generously and frequently, reapplying at least every two hours and after swimming or sweating. It is crucial to combine sunscreen usage with other sun protection measures like seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, and using sunglasses and hats for comprehensive sun protection.
Protect your pets against the heat

Protecting your pets from heat is crucial to ensure their well-being and prevent heat-related illnesses. Here are some important tips to keep your pets safe and comfortable during hot weather:
- Provide shade and shelter: Ensure that your pets have access to shaded areas, either naturally from trees or through the use of canopies, umbrellas, or covered structures. This will protect them from direct sunlight and help keep them cool.
- Fresh water at all times: Always provide an ample supply of fresh, cool water for your pets to drink. Check the water frequently to ensure it hasn’t become hot or evaporated. Consider using a pet water fountain or adding ice cubes to the water to keep it cooler for longer.
- Avoid hot surfaces: Hot pavement, sand, or concrete can burn your pet’s paws. Walk your pets during cooler times of the day or choose shady routes. Test the temperature of surfaces with your hand before allowing your pet to walk on them.
- Limit outdoor activities: During extreme heat, it’s best to limit your pet’s outdoor activities. Avoid exercising or playing in the heat of the day and opt for early mornings or evenings when temperatures are cooler.
- Never leave pets in a parked vehicle: It’s crucial never to leave your pets unattended in a parked vehicle, even for a short period. Temperatures inside a car can rise rapidly and lead to heatstroke, which can be fatal.
- Provide cooling options: Help your pets stay cool by providing them with cooling options. Wet their fur with a misting spray or offer them a shallow pool or a kiddie pool filled with water to splash in. You can also use cooling mats or provide wet towels for them to lie on.
- Avoid intense exercise: Avoid engaging in rigorous or strenuous exercise with your pets during hot weather. Overexertion can lead to overheating and dehydration. Instead, opt for gentle activities and keep a close eye on their energy levels and behavior.
- Watch for signs of heat stress: Be vigilant for signs of heat stress in your pets, which may include excessive panting, drooling, rapid breathing, weakness, vomiting, or collapsing. If you notice any of these symptoms, move your pet to a cool area immediately and contact a veterinarian.
- Grooming and coat care: Regular grooming can help keep your pet’s coat in good condition and prevent matting, which can impede heat dissipation. However, consult with a professional groomer or veterinarian about the appropriate length to trim your pet’s coat, as some breeds rely on their fur for insulation.
- Consult your veterinarian: If you have specific concerns about your pet’s health or well-being in hot weather, it’s always a good idea to consult your veterinarian. They can provide personalized advice based on your pet’s breed, age, and health condition.
By following these guidelines, you can help ensure the safety and well-being of your beloved pets during hot weather conditions.
Protect your house against the heat
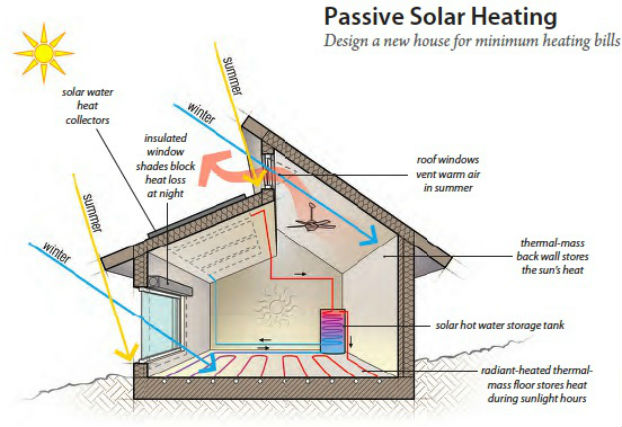
To keep your house cool and comfortable during hot weather, you can take several measures to reduce heat gain and improve ventilation. Here are some tips:
- Use window coverings: Install blinds, curtains, or shades to block out direct sunlight. Light-colored or reflective window coverings can help reflect heat away from your home.
- Insulate your home: Proper insulation in your walls, attic, and roof can help maintain a cooler indoor temperature by preventing heat transfer from the outside.
- Seal air leaks: Check for any gaps or cracks in windows, doors, and walls that can let warm air in. Seal these areas with weatherstripping or caulking to improve energy efficiency.
- Utilize natural ventilation: Open windows and doors during cooler times of the day, such as evenings and early mornings, to let in fresh air. Use window fans or ceiling fans to promote air circulation.
- Use air conditioning efficiently: Set your air conditioner to an appropriate temperature and use programmable thermostats to regulate cooling. Close off unused rooms to concentrate cooling in occupied areas.
- Use fans strategically: Place portable fans in windows or doorways to draw in cooler air from outside. Ceiling fans can help circulate air and create a breeze indoors.
- Optimize landscaping: Plant trees or install awnings outside windows to provide shade and reduce the amount of direct sunlight that enters your home. This can help lower indoor temperatures.
- Minimize heat-generating activities: Avoid using heat-generating appliances during the hottest parts of the day. Cook outdoors on a grill, use energy-efficient lighting, and limit the use of electronics that emit heat.
- Keep interior surfaces cool: Use light-colored or reflective materials for your roof and exterior walls to minimize heat absorption. Consider using shades or reflective films on windows to reduce heat gain.
- Stay hydrated and use personal cooling methods: Keep yourself cool by staying hydrated, using handheld fans, and wearing lightweight, breathable clothing. Use cold compresses or take cool showers to lower your body temperature.
By implementing these strategies, you can help keep your house cooler during hot weather, reducing the need for excessive air conditioning and creating a more comfortable living environment.
10 Free Life Hacks – Keeping it Cool
- Use a Damp Towel on the Fan: Drape a damp towel over a portable fan or box fan. As the air blows through the moist towel, it creates a cooling mist effect.
- Create a DIY Swamp Cooler: Fill a shallow pan or tray with ice and place it in front of a fan. The fan will blow air over the chilled surface, creating a cooling breeze.
- Optimize Your Thermostat: Set your thermostat to a slightly higher temperature and use fans to circulate cool air. This can help reduce energy consumption and still keep your home comfortable.
- Freeze Water Bottles: Freeze water bottles and place them in front of fans or carry them around the house. The frozen bottles will provide a refreshing cool breeze as they thaw.
- Use Natural Cooling Methods: Take advantage of natural cooling methods like evaporative cooling. Place bowls of cold water or wet towels in strategic locations to promote evaporation and cool the air.
- Install Window Awnings: Install retractable or permanent window awnings to provide shade and block direct sunlight from entering your home.
- Create a Cool Sleeping Environment: Use lightweight, breathable bedding and consider cooling pillows or mattress toppers. Keep the bedroom cool by using a fan or utilizing other cooling methods mentioned earlier.
- Seal Air Leaks: Identify and seal any air leaks around windows, doors, and vents to prevent warm air from entering your home and cool air from escaping.
- Cook Outdoors: Avoid using the stove or oven indoors during hot days. Instead, opt for outdoor cooking methods like grilling or using a portable cooktop to minimize heat buildup inside.
- Use Cold Water Sprays: Fill a spray bottle with cold water and mist yourself or the air around you for instant cooling. This can be especially refreshing during hot summer days.
By implementing these additional life hacks, you can further enhance your efforts to keep your house cool and comfortable while reducing reliance on air conditioning and saving energy.

10 Free innovative cooling tips
- Smart thermostats: Consider installing a smart thermostat in your home. These devices allow you to control and schedule your cooling system remotely using a smartphone app. They can learn your preferences and adjust temperature settings automatically to optimize energy efficiency.
- Evaporative cooling: Explore evaporative cooling systems, also known as swamp coolers. They work by drawing warm air through water-saturated pads, which causes the water to evaporate and cool the air. This technology is particularly effective in arid climates.
- Heat pumps: Consider using heat pumps for both heating and cooling. Heat pumps use electricity to move heat from one place to another, providing efficient cooling in summer and heating in winter. They are particularly suitable for moderate climates.
- Geothermal cooling: If feasible for your property, geothermal cooling systems utilize the stable underground temperature to cool your home. They circulate fluid through pipes buried in the ground to extract heat, offering energy-efficient and sustainable cooling.
- Radiant cooling: Explore radiant cooling systems that use chilled water circulated through pipes in walls, ceilings, or floors to cool your living spaces. This method provides a comfortable and energy-efficient cooling solution.
- Solar-powered cooling: Consider incorporating solar panels to power your cooling systems. Solar energy can help offset electricity usage, making your cooling more sustainable and reducing your carbon footprint.
- Energy-efficient air conditioning units: When purchasing air conditioning units, look for models with high energy efficiency ratings. Energy Star-certified models use less energy to operate, resulting in lower electricity bills and reduced environmental impact.
- Automated shading and insulation: Invest in automated shading systems or window films that block heat from entering your home. Additionally, improve insulation in your walls, ceilings, and windows to prevent heat transfer and maintain a cooler indoor environment.
- Natural ventilation: Utilize natural ventilation techniques by strategically opening windows and using fans to create cross breezes. This allows for fresh air circulation and can provide cooling in mild weather conditions.
- Energy monitoring and management: Use energy monitoring systems to track and analyze your cooling energy usage. This can help you identify areas for improvement, adjust settings, and optimize your cooling efficiency.
By exploring these innovative cooling technologies and implementing energy-efficient practices, you can create a more comfortable living environment while minimizing energy consumption and reducing your environmental impact.
Why do Airconditioners turn up the heat?
Air conditioners contribute to the climate impact primarily through their energy consumption and the refrigerants they use. Here are a few ways in which air conditioners can worsen the climate effect:
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Air conditioners, especially older models, typically rely on hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) refrigerants, which are potent greenhouse gases. When released into the atmosphere, these refrigerants contribute to global warming. The production and disposal of air conditioners also emit greenhouse gases.
- Energy Consumption: Air conditioners require a significant amount of energy to operate, especially when cooling large spaces or in areas with high ambient temperatures. The majority of this energy comes from fossil fuel-based power plants, which emit carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases. Increased energy demand for cooling can lead to higher emissions and contribute to climate change.
- Heat Island Effect: The extensive use of air conditioners in urban areas creates the “heat island effect.” Air conditioners release waste heat into the surrounding environment, increasing local temperatures. This effect exacerbates the demand for cooling and can lead to a vicious cycle of higher energy consumption and increased greenhouse gas emissions.
- Deforestation and Land Use: The need for cooling often leads to increased electricity generation, which can drive deforestation for the construction of hydropower dams or the extraction of fossil fuels. Land-use changes contribute to the loss of forests, which are crucial in absorbing CO2 and mitigating climate change.
To mitigate the climate impact of air conditioners, several measures can be taken:

- Energy Efficiency: Investing in energy-efficient air conditioning units can significantly reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Look for models with high Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) or Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) ratings.
- Transition to Low-GWP Refrigerants: Manufacturers are phasing out HFC refrigerants and transitioning to low-global-warming-potential (GWP) alternatives, such as hydrofluoroolefins* (*unsaturated organic compounds composed of hydrogen, fluorine, and carbon) (HFOs). Choosing air conditioners with low-GWP refrigerants can help minimize their climate impact.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Powering air conditioners with clean and renewable energy sources like solar or wind can reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with cooling.
- Improved Building Design: Enhancing building insulation, using reflective materials, and implementing passive cooling techniques can reduce the reliance on air conditioning and lower energy consumption.
By adopting these strategies, it is possible to mitigate the climate impact of air conditioners and move towards more sustainable cooling solutions.
Where to go when it is hot.
When the weather is hot, there are various outdoor places you can consider visiting to enjoy the outdoors while staying cool. Here are some options:
- Beaches: Coastal areas with beaches can provide a refreshing escape from the heat. The combination of water, sand, and sea breeze can help you stay cool and enjoy recreational activities.
- Lakes or Rivers: If you have access to lakes or rivers in your area, they can offer opportunities for swimming, boating, or simply relaxing by the water. These natural bodies of water often provide a cooler environment than the surrounding land.
- Water Parks or Splash Pads: Water parks and splash pads are designed to provide water-based fun for all ages. These recreational areas feature water slides, pools, and interactive water features that can help you cool down and have a great time.
- Public Pools: Many cities and communities have public pools where you can swim and cool off. Check local listings to find nearby pools that offer public access.
- Outdoor Shaded Areas: Seek out parks, gardens, or outdoor spaces with ample shade from trees or canopies. These shaded areas can offer relief from direct sunlight and provide a cooler environment.
- Picnic Areas with Shelters: Look for picnic areas that have shaded shelters or pavilions. These spaces often provide seating, tables, and protection from the sun, allowing you to enjoy a meal or gather with friends and family comfortably.
- Hiking Trails with Shade: Find hiking trails that offer shade through tree cover or natural formations. These trails can provide an opportunity to explore nature while staying cooler in the shade.
- Outdoor Cafes or Restaurants: Look for outdoor dining establishments with shaded seating areas or misting systems. Enjoy a meal or a refreshing drink in a comfortable outdoor setting.
- Botanical Gardens or Arboretums: These serene environments often feature lush greenery and shaded pathways, making them pleasant places to explore and escape the heat.
- Indoor-Outdoor Spaces: Look for venues or attractions that have indoor-outdoor areas where you can enjoy the best of both worlds. These spaces often have shaded outdoor sections with fans or misting systems to keep you cool while still being able to enjoy the outdoors.
Remember to stay hydrated, apply sunscreen, and listen to your body’s signals in hot weather. It’s important to prioritize your comfort and safety while enjoying outdoor activities during hot temperatures.
Ten Heat Facts you might not know about.
Here are ten lesser-known facts about heat:
- Heat travels through conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction occurs when heat transfers through direct contact, convection involves heat transfer through the movement of fluids or gases, and radiation refers to the emission of electromagnetic waves.
- The highest temperature ever recorded on Earth was 134.1°F (56.7°C) in Death Valley, California, USA, on July 10, 1913.
- Heat expands materials. Most substances, including solids, liquids, and gases, expand when heated and contract when cooled.
- The sensation of heat is subjective and influenced by factors such as humidity, air movement, and individual sensitivity.
- Heat lightning is a term used to describe distant lightning flashes that are visible but not accompanied by thunder. It occurs when lightning from a thunderstorm is too far away for the sound to be heard.
- Heat can alter the chemical composition and properties of certain substances. For example, cooking food involves the application of heat, which can transform raw ingredients into new textures and flavors.
- High temperatures can impact electronic devices, causing them to overheat and potentially malfunction. Adequate cooling measures are essential to maintain the optimal performance and longevity of electronics.
- Heatwaves can create urban heat islands, where cities experience significantly higher temperatures compared to surrounding rural areas due to human activities, heat-absorbing materials, and limited green spaces.
- Heatstroke is a severe heat-related illness characterized by a body temperature of 104°F (40°C) or higher. It is a medical emergency and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
- The heat index, also known as the “feels like” temperature, combines air temperature and relative humidity to provide an indication of how hot it feels to the human body. It takes into account the cooling effect of evaporation on the skin.
These fascinating facts shed light on the diverse aspects of heat and its impact on our environment, health, and everyday experiences.
We end this article stark reminder about the sun.
Once upon a time, there was a young and ambitious inventor named Alexios. He possessed a brilliant mind and an insatiable desire to explore the unknown. Alexios had a dream of reaching unimaginable heights and defying the limits of human potential. Inspired by the Greek myth of Icarus, he became obsessed with the idea of flight. Driven by his passion, Alexios dedicated countless hours to his workshop, meticulously crafting a set of magnificent wings. He believed that these wings, made of delicate feathers and secured by a sturdy framework, would enable him to soar through the sky like a bird.
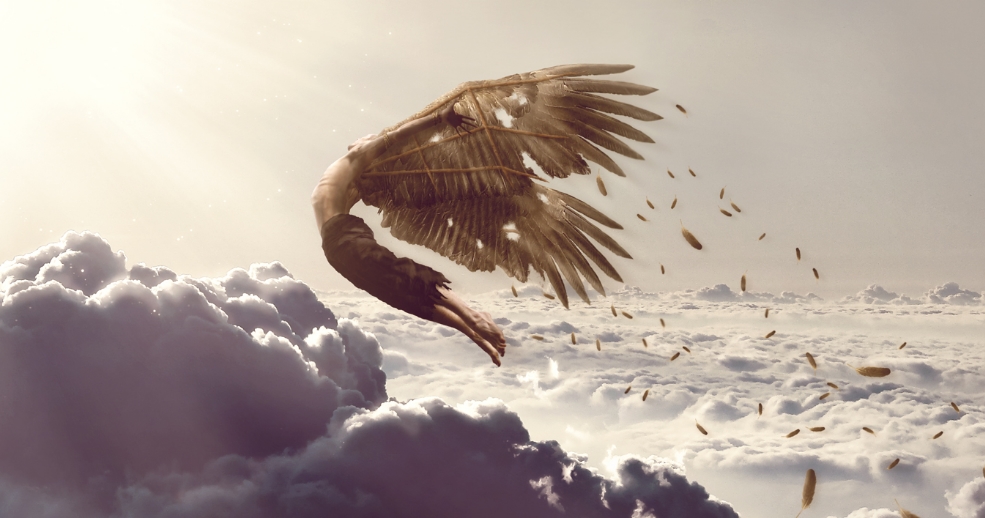

The day of the maiden flight arrived, and Alexios donned his wondrous wings. He stood at the edge of a high cliff, his heart pounding with anticipation. With a leap of faith, he launched himself into the air, feeling the rush of wind against his face. For a moment, it seemed as though Alexios had achieved the impossible. He soared through the heavens, relishing the sensation of freedom and triumph. But as he climbed higher and higher, his jubilation turned into a mixture of excitement and trepidation. Unbeknownst to Alexios, his wings were not designed to withstand the intense heat radiating from the sun. As he flew closer to its scorching rays, the heat grew unbearable, causing the wax that held his wings together to melt away. In a sudden and tragic realization, the once magnificent wings began to disintegrate. Feathers floated helplessly in the air, leaving Alexios in a state of panic and despair. The exhilaration of flight swiftly turned into a desperate battle to save himself from the impending fall. Gravity took hold, and Alexios plummeted towards the earth, desperately flapping the remnants of his wings.
His dreams of conquering the skies shattered as he crashed into the unforgiving ground. Bruised, broken, and humbled, Alexios learned a powerful lesson. His pursuit of greatness had blinded him to the dangers that lay in his path. He had flown too close to the sun, driven by ambition and a desire for glory, only to be brought crashing down by his own hubris. From that day forward, Alexios carried the weight of his failed flight as a constant reminder of the importance of balance, humility, and understanding one’s limitations. His story served as a cautionary tale, warning others not to let their ambitions blind them to the potential consequences of their actions. And so, the tale of Alexios and his ill-fated flight lives on, a timeless reminder of the dangers of reaching too high, too fast, and too close to the sun.
Conclusion: Always Use Sunscreen
Resource: Heat Map Climat Change. How to sleep in the heat,




